- Produits

 Hoskin Environnement
Hoskin EnvironnementInstruments d’échantillonnage et de surveillance de l’air, de l’eau, de la météo et du sol pour les secteurs de l’environnement, de l’agriculture, des mines et de la recherche.

 Hoskin Géotechnique
Hoskin GéotechniqueÉvaluation des matériaux et des produits pour le sol, l’asphalte, le pétrole, le béton, les mines, le ciment et les instituts de recherche.

 Hoskin Instrumentation
Hoskin InstrumentationCapteurs, transducteurs et instrumentation pour le secteur industriel, la fabrication, la recherche et le développement et l’automatisation des usines.
- Applications
- Intégration de systèmes
- Location
- Service
- À propos
Notre entreprise
Nous sommes là où vous avez besoin de nous, partout au Canada.
Nouvelles
Se tenir au courant de l’information sur les nouveaux produits et des innovations dans l’ensemble des applications que nous soutenons.
Nos bureaux
Hoskin Scientifique offre une couverture nationale sans dénaturer l’offre locale à partir de quatre succursales principales stratégiquement situées à travers le Canada.
- Ressources
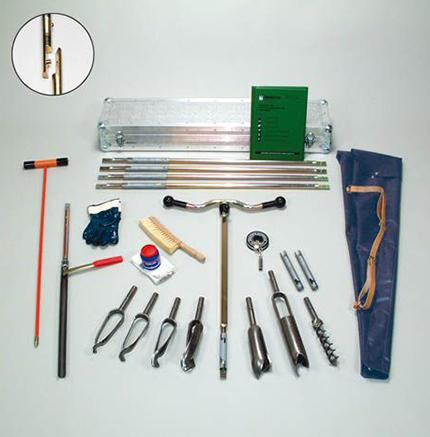


 Posez une question sur ce produit
Posez une question sur ce produit