Canada’s Instrumentation Leader Since 1946.


The sharp increase in the characteristic current-voltage curve for Zener diodes above the breakdown voltage makes it suitable for stabilising small direct voltages. When the input voltage is increased beyond the breakdown voltage, the current increases sharply while the diode resistance gets smaller and smaller. Therefore, the voltage at the Zener diode remains nearly constant.
Principle
The sharp increase in the characteristic current-voltage curve for Zener diodes above the breakdown voltage makes it suitable for stabilising small direct voltages. When the input voltage is increased beyond the breakdown voltage, the current increases sharply while the diode resistance gets smaller and smaller. Therefore, the voltage at the Zener diode remains nearly constant.
A resistor must be insert to ensure that the maximum allowable dissipation power for the Zener diode is not exceeded.
If a load resistor is connected in parallel to the Zener diode, the current flowing through the Zener diode is reduced in favour of the load current. Stabilisation is interrupted when there is no more current flowing through the Zener diode. For this reason, the use of Zener diodes is limited to relatively small load currents. Electronic regulation circuits are used for larger loads.
There is a closely graduated selection of Zener diodes in the voltage range of 3 V to 200 V, meaning that there are diode types for any desired voltage.
Benefits
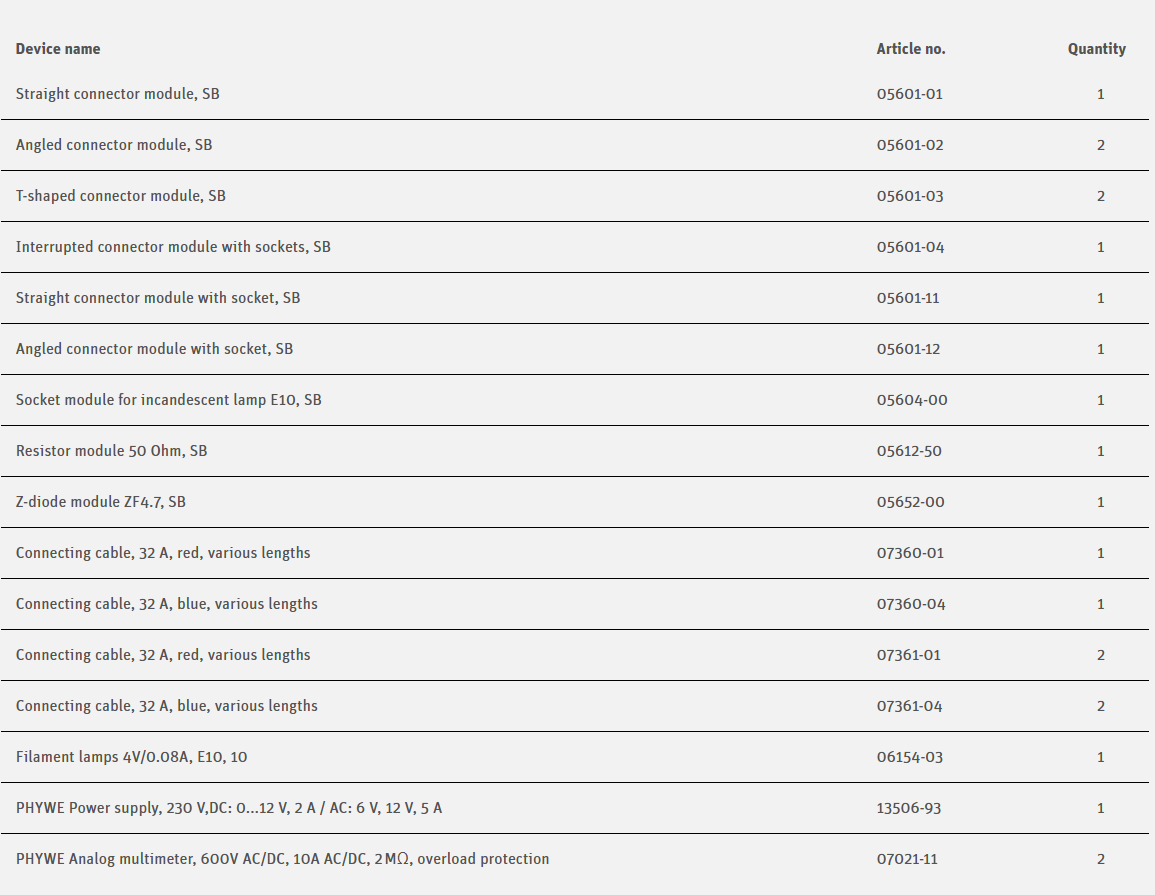
Tasks
How can a Zener diode be used to stabilise direct voltage?
Investigate the functioning of a voltage stabiliser with a Zener diode.
Copyright - 2026 - Hoskin Scientific